Home > Perform Exchange Online Migrations > Prepare for Migrations
Export to PDFPrepare for Migrations
Before performing Exchange Online Migrations in Fly, follow the instructions below to prepare for the migration.
-
Exchange Online Migration requires the availability of Exchange PowerShell for specific functions. Refer to Working with Exchange PowerShell for more details.
-
Make sure the allowed item size of destination mailboxes is sufficient for the migration.
-
Make sure the maximum received message size of the destination mailboxes is sufficient.
Fly provides a script for you to easily configure the size for multiple mailboxes.
-
Click and find the SetMaxReceiveAndSendSize.ps1 script and MailAddressList.csv file.
-
Download the SetMaxReceiveAndSendSize.ps1 script and MailAddressList.csv file to the machine where you want to execute the script.
-
Open the MailAddressList.csv file, and configure the email addresses of mailboxes in the MailAddress column and the size you want to set for the mailbox in the MaxReceiveSizeMB column.
-
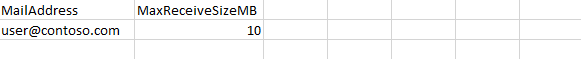
-
Save the file.
-
Locate and execute the SetMaxReceiveAndSendSize.ps1 script using Windows PowerShell.
-
When the execution completes, you can view the report in the directory displayed in the window.
-
-
Fly can remove source sensitivity labels and apply destination labels to emails with a corresponding option selected in the migration policy. Before using this feature, make sure to review the necessary requirements and additional information. Refer to Information about Managing Sensitivity Labels for details.
-
Fly does not automatically provision new users in Microsoft 365. Make sure the destination users already exist before the migration.
NOTEWhen the destination is a Microsoft 365 Multi-Geo tenant, and you want to provision a mailbox for a user in a specific location, you need to set the preferred data location for the user. Then, after the license is assigned to the user, the mailbox will be provisioned in the user’s preferred data location.
There are different ways to add new Microsoft 365 users:
-
Adding users individually. See instructions .
-
Adding users in bulk. See instructions .
-
Adding users via PowerShell. See instructions .
-
Synchronizing users from local Active Directory to Microsoft 365 via Microsoft Entra Cloud Sync. Refer to Synchronize users via Microsoft Entra Cloud Sync for details.
-
Synchronizing users from local Active Directory to Microsoft 365 via Microsoft Entra Sync or Microsoft Entra connect. Refer to Synchronize users via Microsoft Entra Sync or Microsoft Entra Connect for details.
-
-
To avoid destination users from viewing the newly added email addresses in the destination global address list (GAL) when the source mailboxes are still in use, and destination mailboxes are not put in use, you can refer to the following steps to hide users’ email addresses from the destination global address list:
NOTEOnly user/shared/resource/Microsoft 365 Group mailboxes can be hidden from the destination global addresses list.
-
Click and find the HiddenUserOrGroupFromGAL.ps1 script and HiddenUserOrGroupList.csv file.
-
Download the HiddenUserOrGroupFromGAL.ps1 script and HiddenUserOrGroupList.csv file to the machine where you want to execute the script.
-
Open the HiddenUserOrGroupList.csv file, configure the email addresses and mailbox types of users/groups in the Address and Type columns as the screenshot shown below.
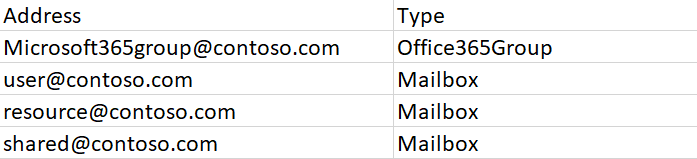
-
Save the file.
-
Locate and execute the HiddenUserOrGroupFromGAL.ps1 script using Windows PowerShell.
-
Enter H and press Enter on the keyboard to enable the HiddenFromAddressListsEnabled command to hide users from the destination GAL. Refer to for details about the command.
-
Enter H and press Enter on the keyboard to enable the HiddenFromExchangeClientsEnabled command to hide groups from the destination GAL. Refer to for details about the command.
-
When the execution completes, you can view the HiddenUserOrGroupList_Report_(TimeStamp).csv file generated in the directory displayed in the window.
NOTEThe execution will have no impact on the email address that has been hidden.
-
-
If you want to synchronize the email addresses in the source Exchange global address list (GAL) to the destination, Fly provides the scripts to synchronize them. Note that the scripts can be used to sync the mail contacts in global contacts. If you want to migrate global contacts, sync the mail contacts first.
Complete the following steps to synchronize the source global address list to the destination:
You can also delete the successfully synchronized source email addresses from the destination global address list.
To delete the successfully synchronized source email addresses, refer to the following steps:
Synchronize users via Microsoft Entra Cloud Sync
Before synchronizing users, you need to complete the prerequisites for Microsoft Entra cloud synchronization and install the Microsoft Entra Cloud. Refer to and for details.
Then, you can refer to the following sections to synchronize users.
Configure Microsoft Entra Cloud Sync
Refer to to configure Microsoft Entra Cloud Sync for provisioning from Active Directory to Microsoft Entra ID.
Configure Attribute Mapping
Refer to the following steps to map attributes between your on-premises user or group objects and the objects in Microsoft Entra ID:
-
Log in to Microsoft Entra admin center (or Azure portal) and navigate to Microsoft Entra ID.
-
Click Microsoft Entra Connect in the left panel. The Get started page appears.
-
On the Get started page, click Cloud Sync in the left panel. The Configurations page appears.
-
Click the desired configuration and click Attribute mapping in the left panel.
-
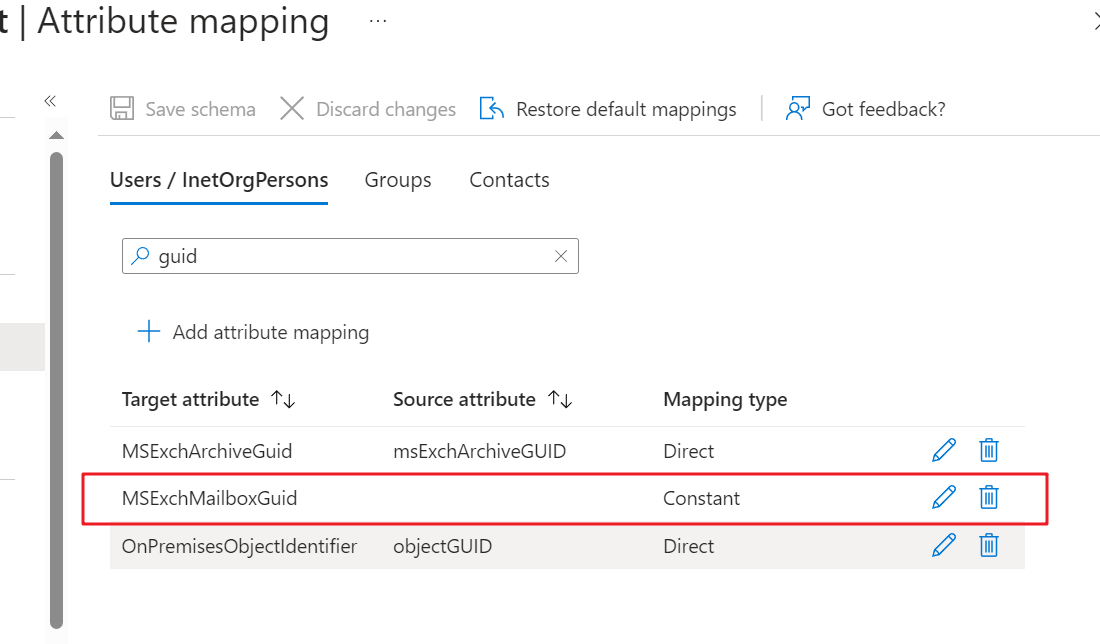
Search MSExchMailboxGuid under the Users / InetOrgPersons tab.
-
Click the Edit attribute mapping (
 ) button. The Edit attribute mappings page appears.
) button. The Edit attribute mappings page appears. -
Select Expression from the Mapping type drop-down list, enter "" in the Expression text box, and click Apply.
-
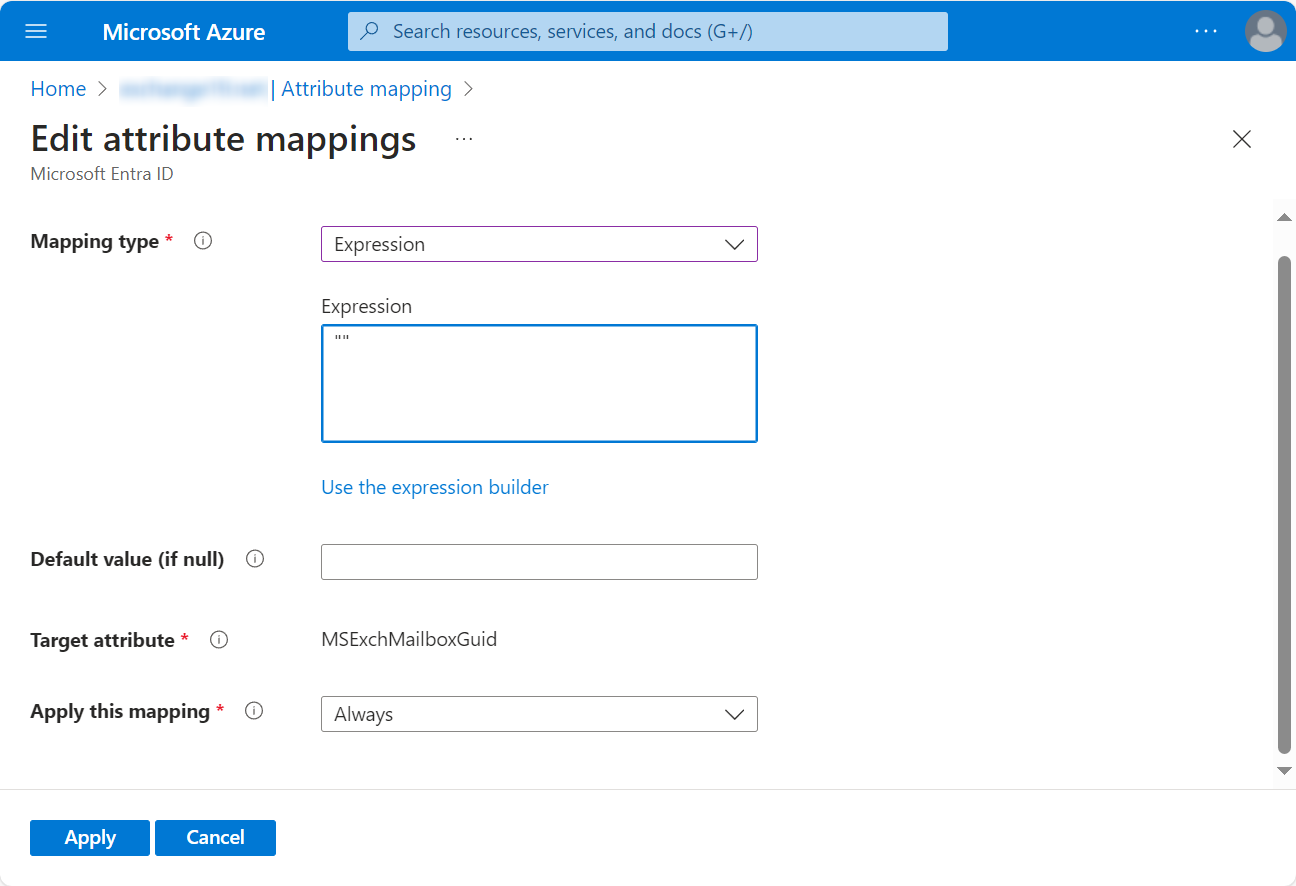
-
Check to make sure the source attribute of MSExchMailboxGuid is empty.
-
Configure Scoping Filters
Refer to the following steps to configure a scoping filter to define the synchronization scope:
-
Log in to Microsoft Entra admin center (or Azure portal) and navigate to Microsoft Entra ID.
-
Click Microsoft Entra Connect in the left panel. The Get started page appears.
-
On the Get started page, click Cloud Sync in the left panel. The Configurations page appears.
-
Click the desired configuration and click Scoping filters in the left panel.
-
Select the synchronization scope. If you select Selected security groups or Selected organizational units, enter the corresponding distinguished name in the text box. To get the distinguished name of a security group or organizational unit, refer to the Get the Distinguished Name using Windows PowerShell section below.
-
Click Add to add the distinguished name and click Save to save the scoping filters.
Get Distinguished Names using Windows PowerShell
Refer to the following instructions to get the distinguished name of a security group or organizational unit:
On-demand Provisioning (Optional)
Refer to to check whether users in the synchronization scope can be correctly synchronized to Microsoft Entra ID.
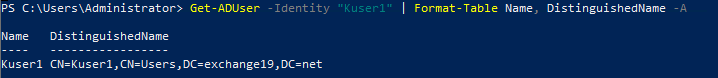
To get the distinguished name of a user, open Windows PowerShell and enter the following command:
Get- ADUser -Identity "Kuser1" | Format-Table Name, DistinguishedName -A
Replace Kuser1 with the display name of the user and press Enter on the keyboard.
Synchronize Users
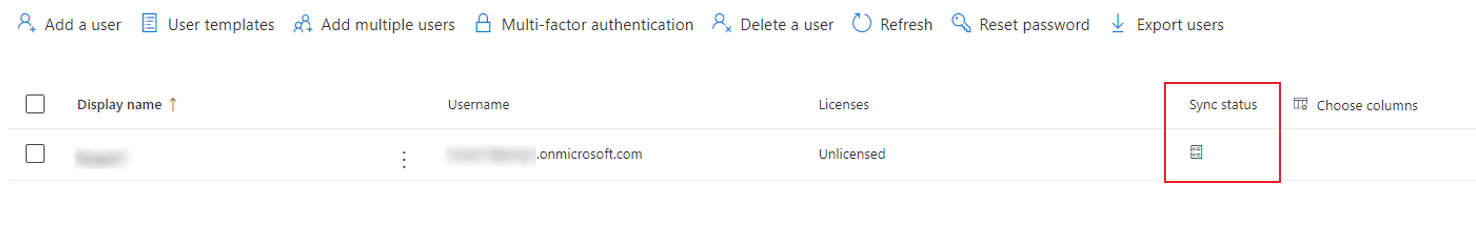
Refer to to synchronize users. Then, you can check the sync status of users in Microsoft 365 admin center > Users > Active users. After assigning Exchange Online license to the user, the mailbox of the user will be automatically initialized.
Synchronize users via Microsoft Entra Sync or Microsoft Entra Connect
Refer to the following sections to synchronize users from local Active Directory to Microsoft 365 via Microsoft Entra Sync or Microsoft Entra connect:
Synchronize All Users
Refer to the following steps to synchronize all users:
-
Install Microsoft Entra Sync or Microsoft Entra Connect (if you need support for federation).
NOTEMake sure msExchMailboxGuid is set to Null before the synchronization. Only after you change the msExchMailboxGuid attribute value can a user mailbox be created when an Exchange license is assigned.
To set the msExchMailboxGuid to Null, complete the following steps. Note that the following steps will synchronize all users from the local Active Directory to Microsoft 365. If you only want to synchronize a part of the users to Microsoft 365, refer to Set a Filter Rule and Synchronize Included Users below to set a filter rule and only synchronize the users included in the filter rule.
-
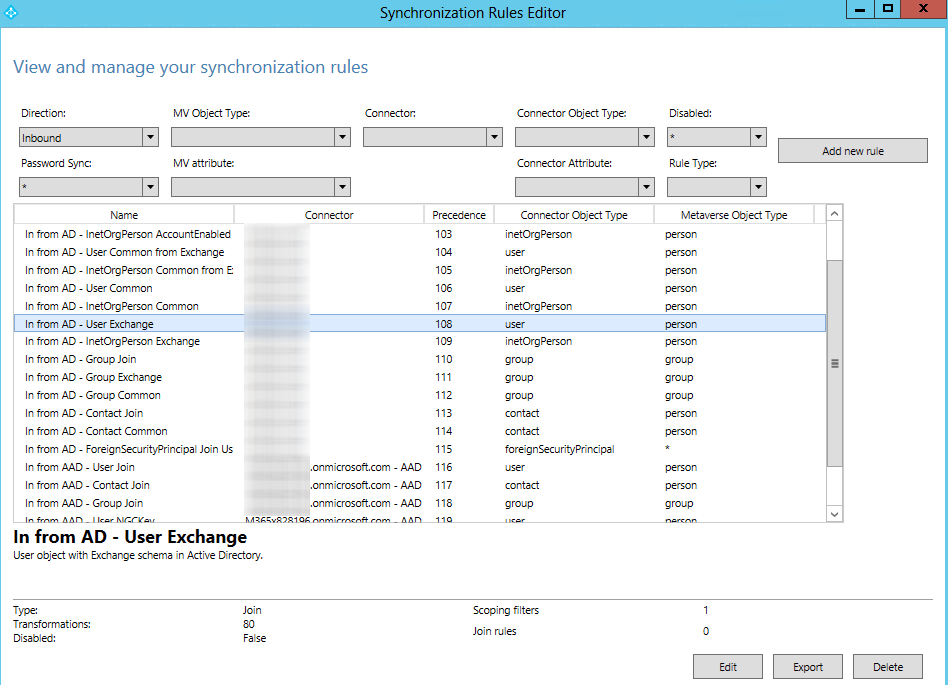
Run the Synchronization Rules Editor as an administrator.
-
Select In from AD – User Exchange and click Edit.
-
In the pop-up window, click Yes to edit the current rule.
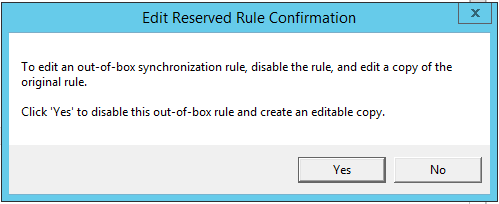
-
In the Edit Inbound Synchronization Rule window, change the Precedence value to 1.
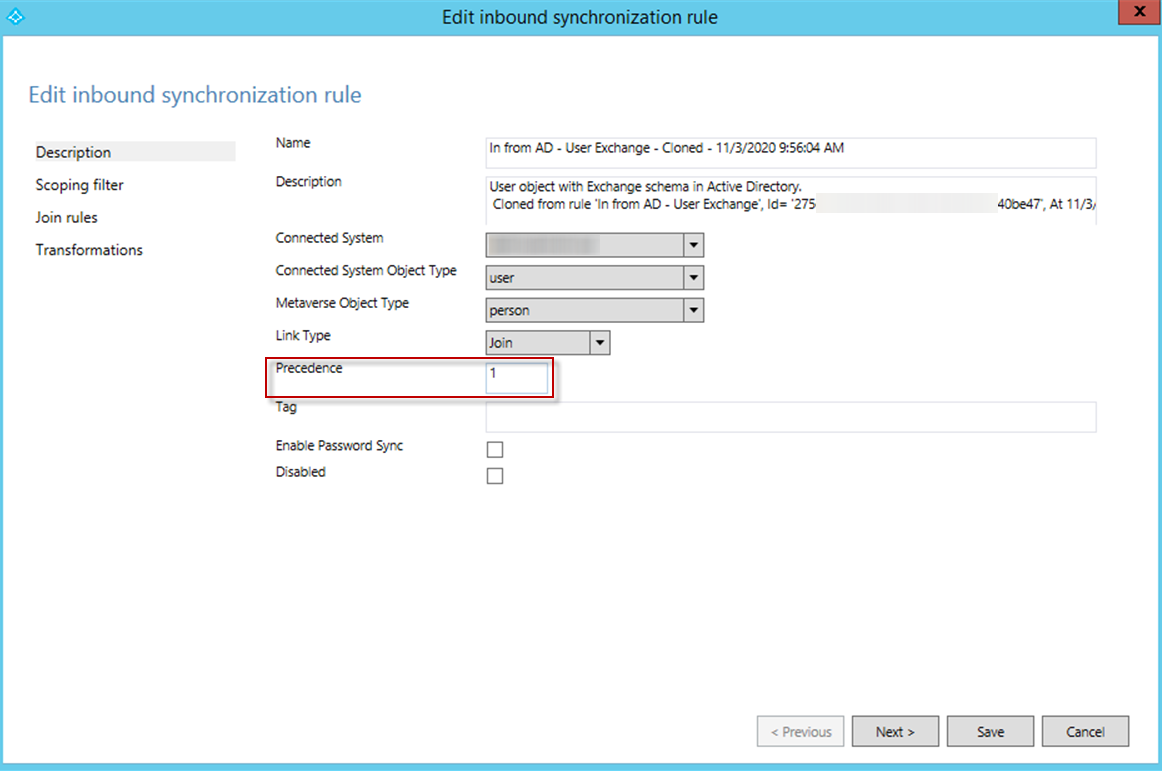
-
Select Transformations in the left pane, and find the msExchMailboxGuid attribute.
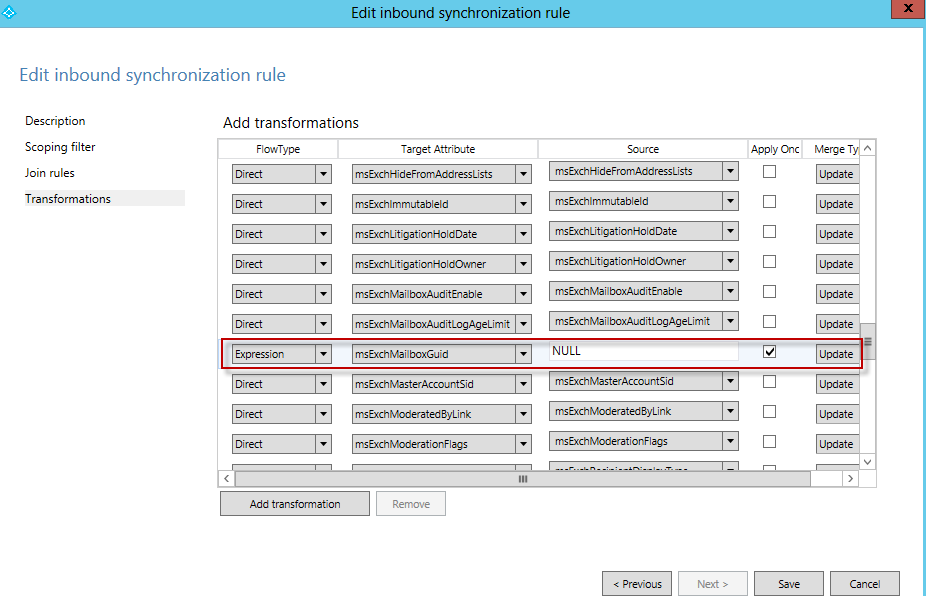
-
Complete the following settings for the msExchMailboxGuid attribute:
-
Select Expression for the FlowType column.
-
Enter NULL for the Source column.
-
Select the Apply Once checkbox.
-
Select Update.
-
-
Click Save to save the settings. The In from AD – User Exchange – Cloned rule is automatically created, and the original In from AD – User Exchange rule is automatically disabled.
-
-
Run Microsoft Entra Sync or Microsoft Entra Connect to synchronize users from the local Active Directory to Microsoft 365.
-
After the synchronization, re-enable the original In from AD – User Exchange rule using the Synchronization Rules Editor. Refer to the following steps to re-enable the original In from AD – User Exchange rule:
-
Run the Synchronization Rules Editor as an administrator.
-
Select In from AD – User Exchange – Cloned and click Delete.
-
In the pop-up window, click Yes to delete the current rule.
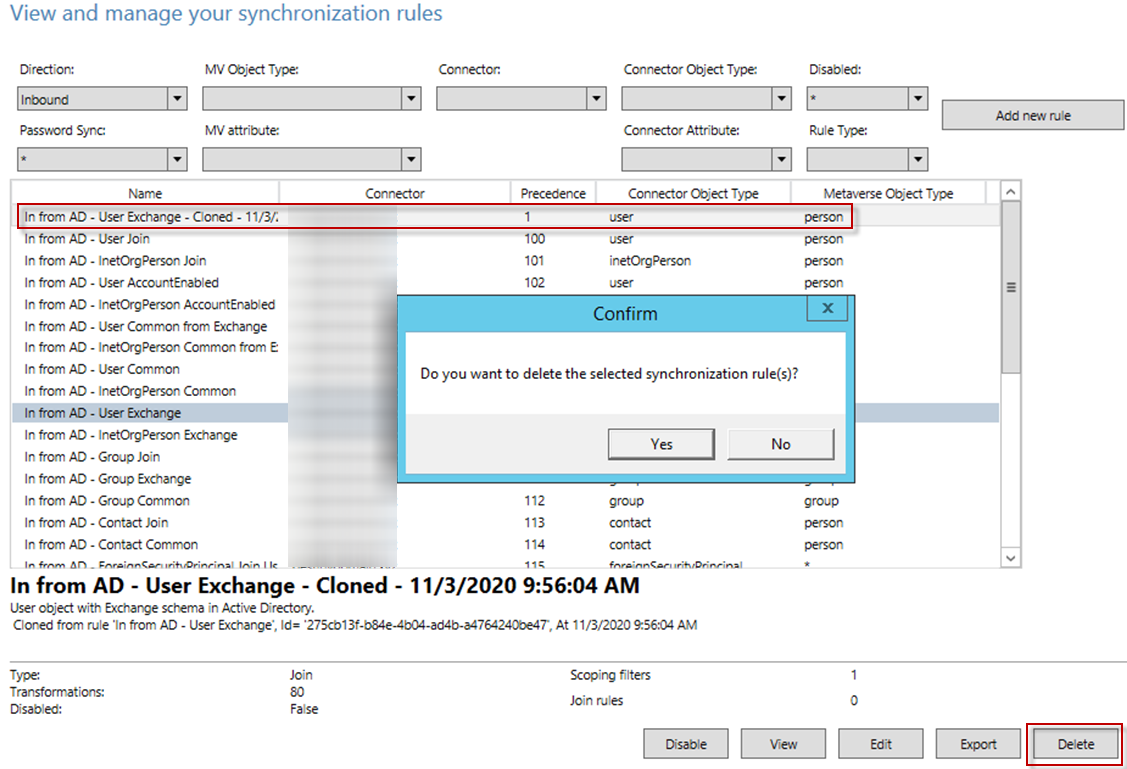
-
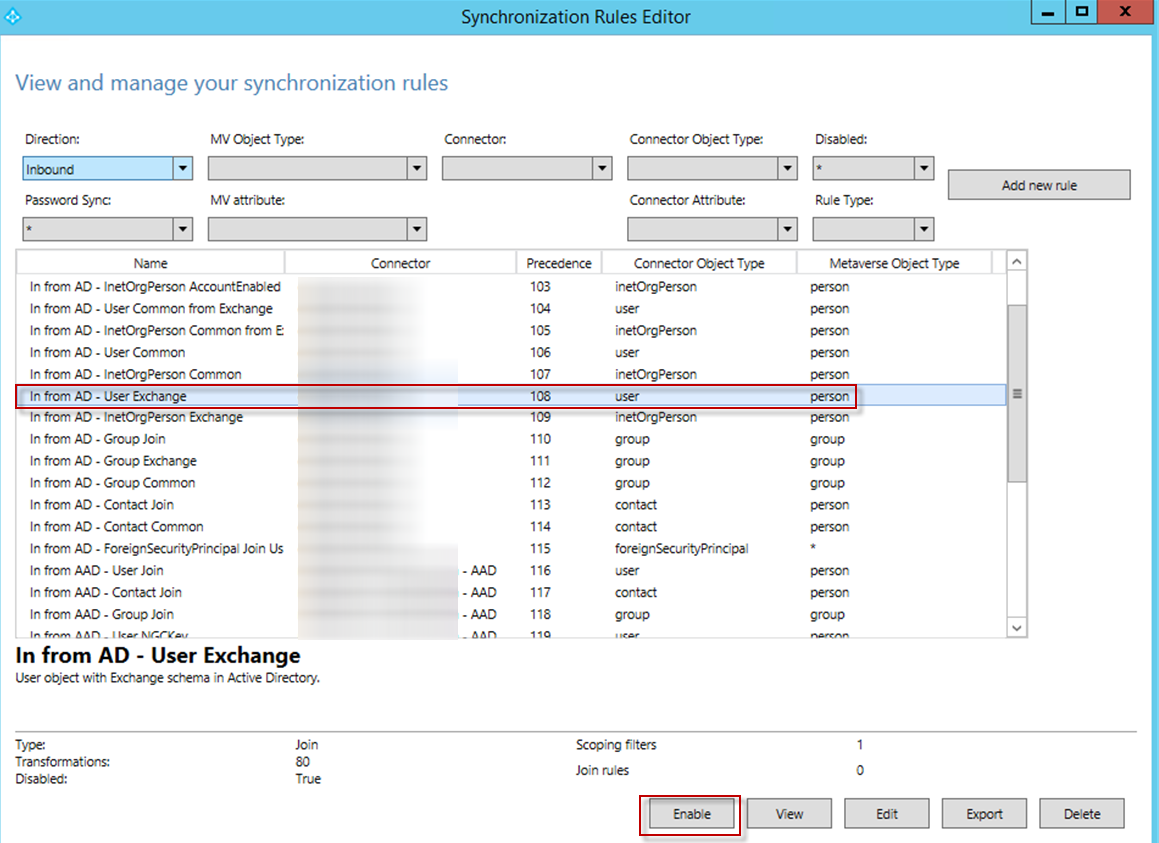
Select the original In from AD – User Exchange rule and click Enable.
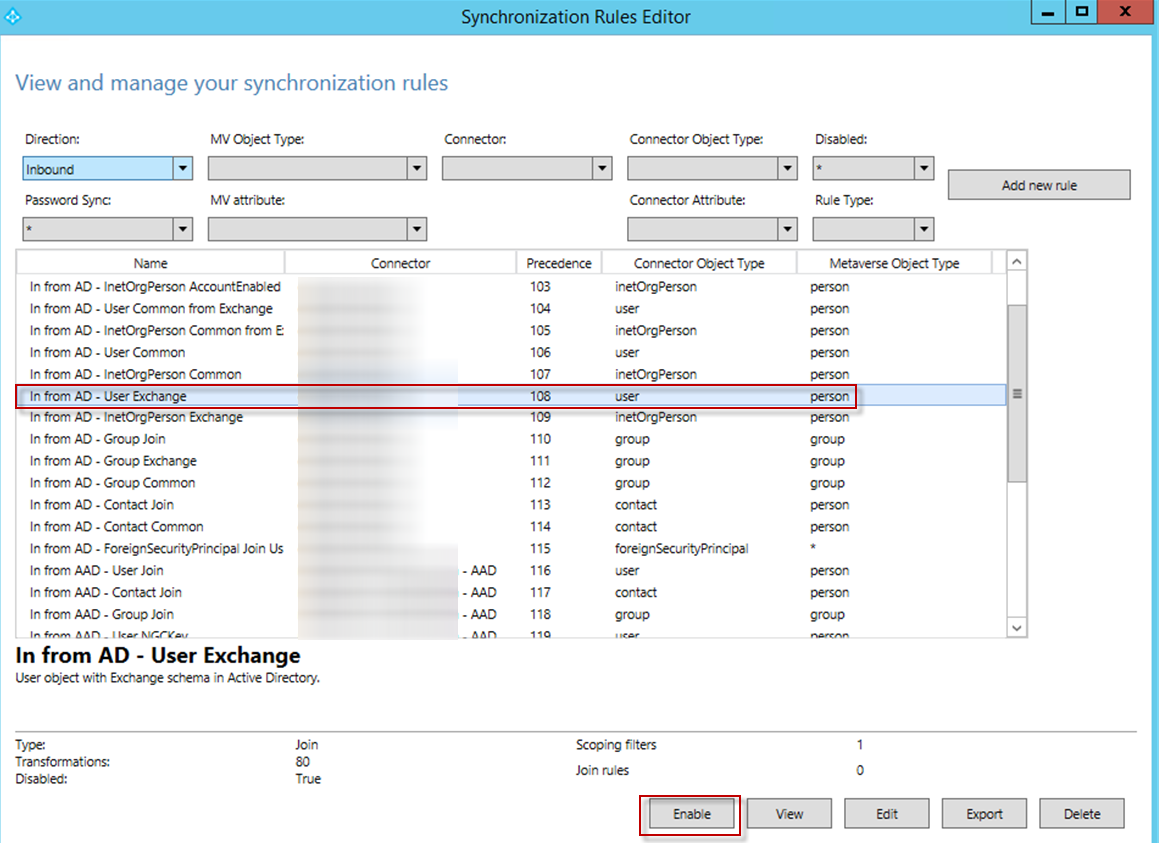
-
Assign Exchange Online licenses to the users.
-
Set a Filter Rule and Synchronize Included Users
Refer to the following steps to set the filter rule and only synchronize the users included in the filter rule:
-
In the Exchange Admin center, edit the mailbox whose user you want to synchronize, choose a custom attribute for the mailbox and specify a tag for the mailbox. For example, choose attribute 5 and enter FLYMigration as the tag.
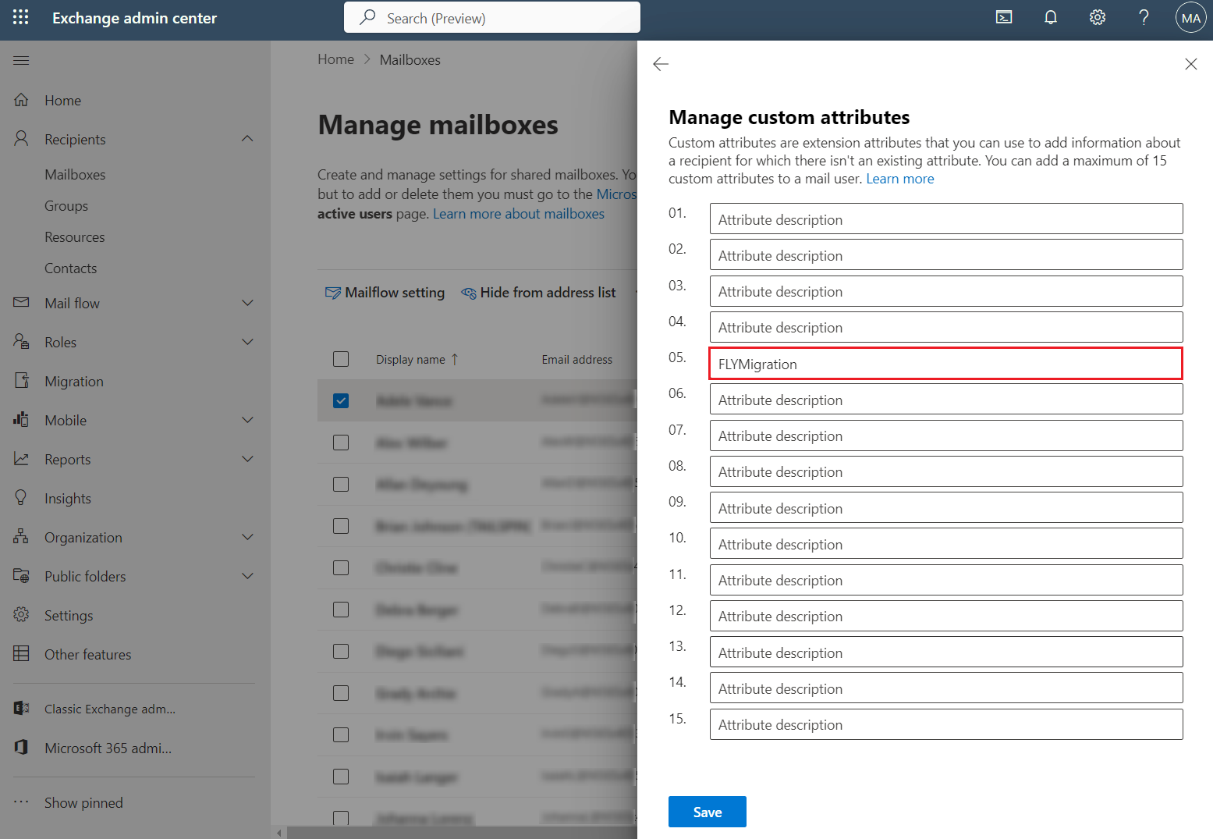
Repeat this step to add the custom attribute for more mailboxes.
To add the custom attribute for mailboxes in bulk, you can also run PowerShell as an administrator, and configure the
Set-Mailbox <email address> -customAttribute “attributevalue”command for each mailbox by defining the mailbox email address, custom attribute number, and custom attribute value. Refer to the screenshot below, for example:
-
Run the Synchronization Rules Editor as an administrator.
-
Select In from AD – User Exchange and click Export to export the rule to a .txt file. Edit the file extension to change the .txt file to a .ps1 file.
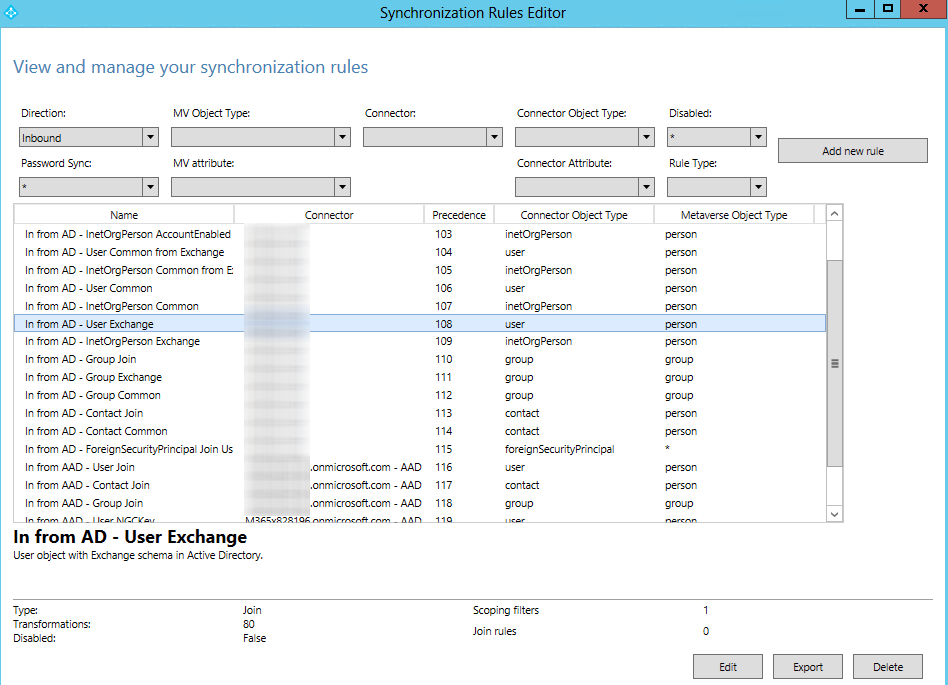
-
Open the exported .ps1 file, customize the Name attribute, change the Precedence attribute value to equal or less than 100, and delete the identifier and ImmutableTag attributes.
-
Run the exported .ps1 file with Windows PowerShell to create the rule in Synchronization Rules Editor.
-
Select the newly created rule and click Edit.
-
Select Scoping filter and click Add clause to add the filter condition. Choose the extensionAttribute5 under Attribute. Select EQUAL under Operator and enter FLYMigration as the attribute value.
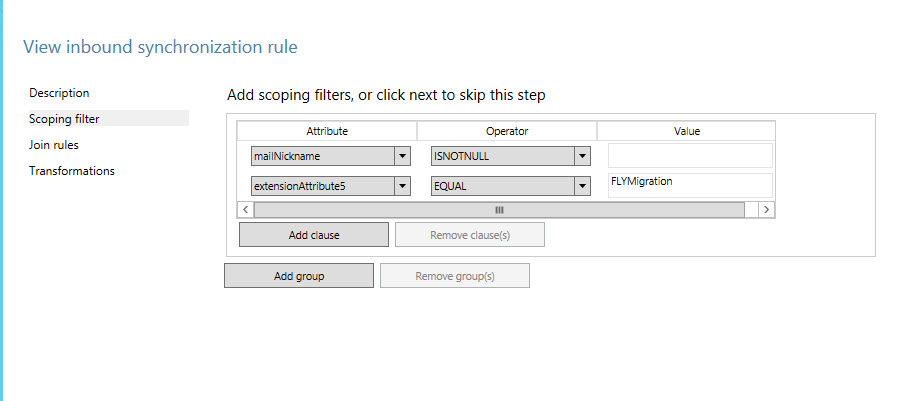
Repeat this step to add more filter conditions according to step a.
-
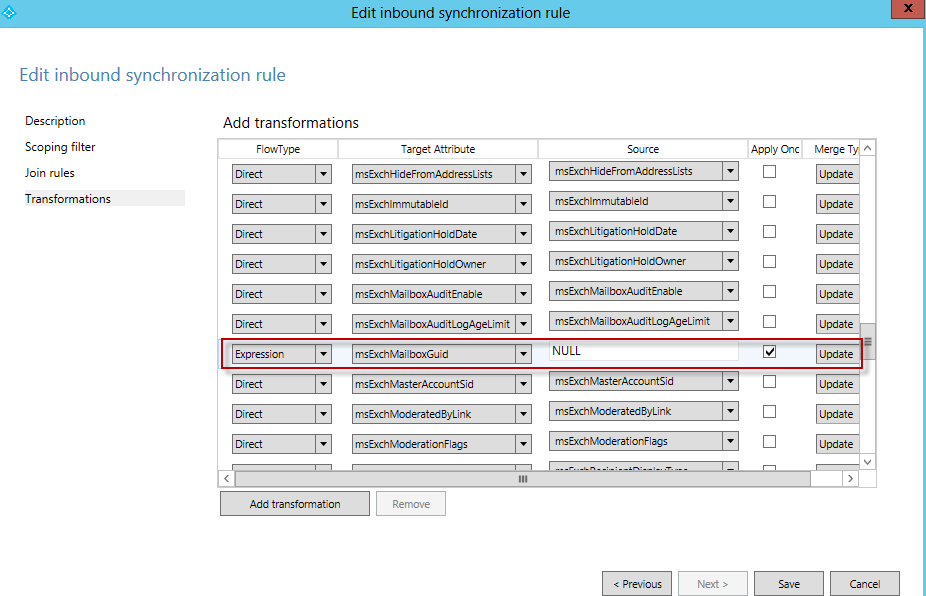
Select Transformations in the left pane, and find the msExchMailboxGuid attribute.
-
Complete the following settings for the msExchMailboxGuid attribute:
-
Select Expression for the FlowType column.
-
Enter NULL for the Source column.
-
Select the Apply Once checkbox.
-
Select Update.
-
-
Click Save to save the settings.
-
Select the original In from AD – User Exchange synchronization rule, and click Edit to edit the rule.
-
In the pop-up window, click Yes to edit the rule.
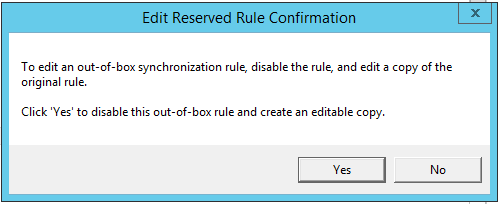
The In from AD – User Exchange – Cloned rule is automatically created, and the original In from AD – User Exchange rule is automatically disabled.
-
Select Scoping filter and click Add clause to add the filter condition. Choose the extensionAttribute5 under Attribute. Select NOTEQUAL under Operator and enter FLYMigration as the attribute value.
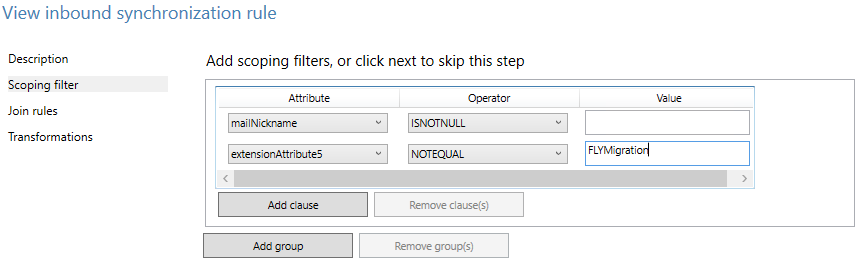
Repeat this step to add more filter conditions according to step a.
-
Click Save to save the settings.
-
Run Microsoft Entra Sync or Microsoft Entra Connect to synchronize users from the local Active Directory to Microsoft 365. Only the mailbox users included in filter conditions are synchronized.
-
After the synchronization, re-enable the original In from AD – User Exchange rule using the Synchronization Rules Editor. Refer to the following steps to re-enable the original In from AD – User Exchange rule:
-
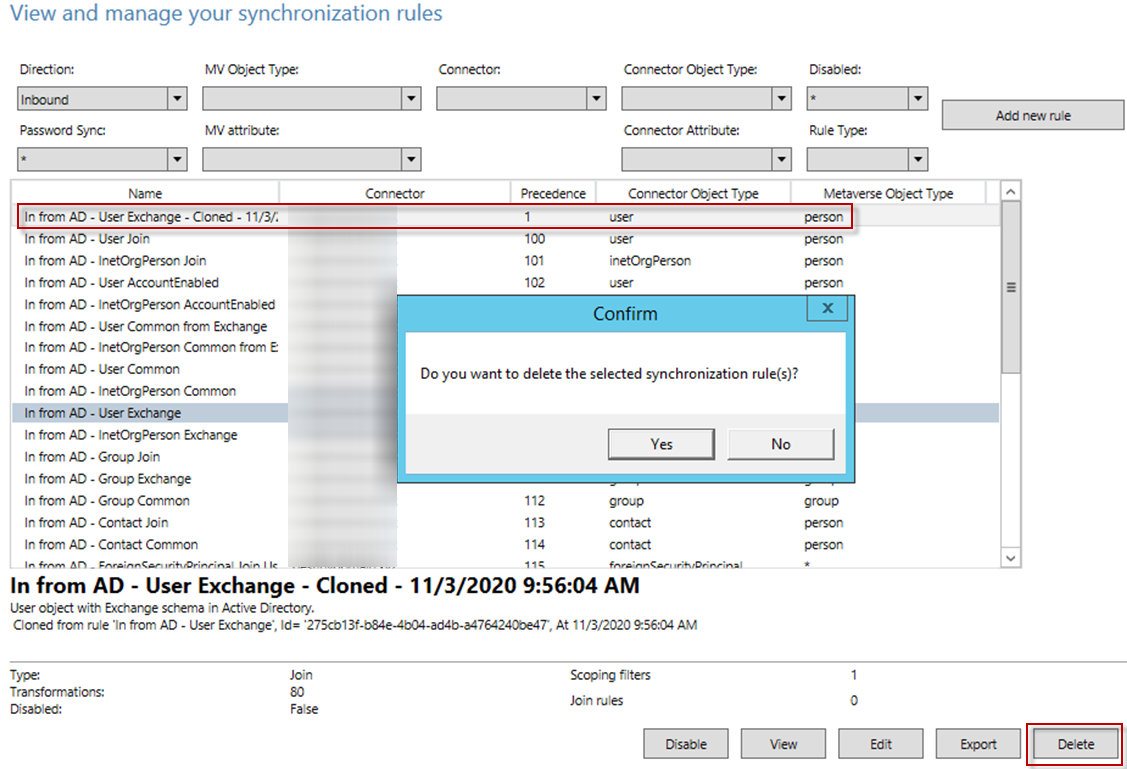
Run the Synchronization Rules Editor as an administrator.
-
Select In from AD – User Exchange – Cloned and click Delete.
-
In the pop-up window, click Yes to delete the current rule.
-
Select the original In from AD – User Exchange rule and click Enable.
-
Assign Exchange Online licenses to the users.
-
