Home > User Guide > Configure General Settings for Backup > Configure Custom Storage Location for Your Backup Data
Export to PDFConfigure Custom Storage Location for Your Backup Data
To view the information about the storage location where your backup data resides, navigate to Settings > General > Storage location.
If you are currently using the Default storage location and you want to use your own storage afterward, you can contact AvePoint support to update your subscription, and then follow the steps below to change the storage location to your own storage.
*Note: The changes from the default storage to a custom storage cannot be reverted, and the custom storage cannot be changed to another custom storage once saved.
-
In your own storage location, for security concerns, the storage firewall may have been set up to only allow trusted clients. To ensure the Cloud Backup for Google Workspace service can access your storage, you must complete the corresponding settings in Allow AvePoint Agent Servers to Access Your Storage Account.
-
Navigate to Settings > General > Storage location and click Change to my own storage.
-
In the Change to my own storage pop-up window, to decide how to handle the existing backup data on the default storage, choose an option from the following:
-
Retain all backup data currently stored in AvePoint’s storage until the retention time expires – The backup data in the default storage location will be retained until the retention time expires. The next backup job for each of the services in the protected scope will store the backup data in the configured custom storage location.
-
Remove all backupdata from AvePoint’s storage – The backup data will be removed from the default storage location, and you cannot use the previous backup data to restore. After the storage location is changed, the backup jobs for services in the protected scope will start in a few seconds. The backup data will be stored in the configured custom storage location.
*Note: After you have changed the storage location, the backup data on the previous storage location will follow the current Retention policy.
-
-
Click OK to save the settings.
Refer to the instructions in the following sections to configure the custom storage location.
*Note: For the best network performance, we strongly recommend you use the Azure storage that is in the same data center as one of your tenants in AvePoint Online Services. Using other storages may cause higher network costs for restore.
Allow AvePoint Agent Servers to Access Your Storage Account
Complete the following settings based on your scenario:
*Note: If you are using a trial subscription and the storage account you want to use in the trial has a firewall enabled, read the conditions below and contact AvePoint Support for the corresponding reserved IP addresses or ARM VNet IDs.
Add Reserved IP Addresses
Follow the steps below:
-
Navigate to AvePoint Online Services interface > Administration > Security to download the list of reserved IP addresses of AvePoint Online Services. For details, refer to the section in the AvePoint Online Services user guide.
-
Navigate to the storage account that you want to secure.
-
Select Networking on the menu.
-
Check that you’ve selected to allow access from Selected networks.
-
Enter the IP address or address range under Firewall > Address Range.
-
Select Save to apply your changes.
Add ARM Virtual Networks
You can refer to the section in the AvePoint Online Services user guide to get the VNet IDs for your data center. There are two ways to add ARM virtual networks:
az storage account show --resource-group $DESTRG --name $DESTSTA --query networkRuleSet.defaultAction
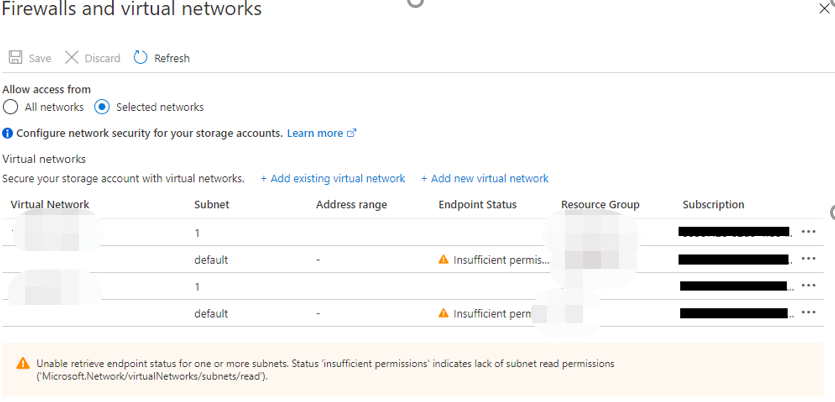
You will see the virtual network rules in Azure Portal, as the screenshot below shows. You may also notice that a warning message “Insufficient Permission…” is displayed. It is because the subnet is not in your subscription. You can ignore it.
Google Cloud Storage
Follow the instructions below:
-
Storage type – Select Google Cloud Storage from the drop-down list.
-
Service account email – Enter the email address of a service account that has the permission to access your bucket.
-
Private key – Enter a private key that is associated with the service account.
-
Project ID – Enter the ID of a project that is associated with your bucket.
-
Bucket name – Enter a bucket name.
-
Advanced – If you want to configure extended parameters, select the Advanced option. Refer to the instructions below to configure Extended parameters, and note that if you have multiple parameters to enter, use the semicolon (;) to separate the parameters.
-
Projection – Customize the projections that can be specified as options in various operations. You can set this value to Full if you want to include all properties, or set this value to NoAcl if you want to omit the ACL (Access Control List) property.
-
PredefinedAcl – Customize a pre-defined ACL of the bucket for simple access control scenarios. The following values are available for this parameter:
-
AuthenticatedRead – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access and all authenticated users get reader access.
-
Private – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access.
-
ProjectPrivate – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access, and project team members get access according to their roles.
-
PublicRead – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access, and all users get reader access.
-
PublicReadWrite – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access, and all users get writer access.
-
-
PredefinedDefaultObjectAcl – Customize predefined access control lists (ACLs) that can be specified when creating or updating objects. The following values are available for this parameter:
-
AuthenticatedRead – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access and all authenticated users get reader access.
-
BucketOwnerFullControl – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access and all authenticated users get reader access.
-
BucketOwnerRead – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access and project team owners get reader access.
-
Private – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access.
-
ProjectPrivate – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access and project team members get access according to their roles.
-
PublicRead – This value represents that the object owner gets owner access and all users get reader access.
-
-
Prefix – Set this value to the string which the bucket name starts with.
-
-
Click Save to save the custom storage location.
Amazon S3
Note that AvePoint will store your backup data to the S3 Standard storage class automatically. You can move the backup data from S3 Standard to S3 Standard-IA, S3 One Zone-IA, or S3 Intelligent-Tiering, and Cloud Backup for Google Workspace can restore the backup data of those storage classes. However, it is not recommended to activate the archive access tier if you are using S3 Intelligent-Tiering. Activating the archive access tier will cause data object files that have not yet been accessed for 90 days to be archived, and Cloud Backup for Google Workspace cannot access the archived data in your Amazon S3 storage.
Follow the instructions below:
-
Storage type – Select Amazon S3 from the drop-down list.
-
Bucket name – Enter a name for the bucket you want to access or create.
-
Access key ID – Enter the corresponding access key ID to access the specified bucket. You can view the access key ID from your AWS account.
-
Secret access key – Enter the corresponding secret key ID to access the specified bucket. You can view the secret key ID from your AWS account.
-
Storage region – Select the storage region of this bucket from the drop-down list.
-
Advanced – If you want to configure extended parameters, select the Advanced option. Refer to the instructions below to configure Extended parameters, and note that if you have multiple parameters to enter, use the semicolon (;) to separate the parameters.
-
RetryCount – Customize the reconnection times after the network connection is interrupted. Enter any positive integer from 0 to 2147483646. For example, RetryCount=6 represents when the network connection is interrupted, and it can reconnect at most 6 times.
If you do not configure this parameter, the value is 6 by default.
-
RetryMode – Customize the retry mode for the requests not being completed successfully. If this parameter is not configured or configured incorrectly, the Legacy will be applied as the default value. You can also set the value to Standard or Adaptive. Standard represents the standardized request retry strategy which is consistent across all SDKs; Adaptive represents an experimental request retry strategy that builds on the Standard strategy and introduces congestion control through client-side rate limiting.
-
-
Click Save to save the custom storage location.
Amazon S3-Compatible Storage
Follow the instructions below:
-
Storage type – Select Amazon S3-Compatible Storage from the drop-down list.
-
Bucket name – Enter a name for the bucket you want to access or create.
-
Access key ID – Enter the corresponding access key ID to access the specified bucket.
-
Secret access key – Enter the corresponding secret access key to access the specified bucket.
-
Endpoint – Enter the URL used to connect to the place where you want to store the data.
-
Advanced – If you want to configure extended parameters, select the Advanced option. Refer to the instructions below to configure Extended parameters, and note that if you have multiple parameters to enter, use the semicolon (;) to separate the parameters.
-
RetryCount – Customize the reconnection times after the network connection is interrupted. Enter any positive integer from 0 to 2147483646. For example, RetryCount=6 represents when the network connection is interrupted, it can reconnect at most 6 times.
If you do not configure this parameter, the value is 6 by default.
-
RetryMode – Customize the retry mode for the requests not being completed successfully. If this parameter is not configured or configured incorrectly, the Legacy will be applied as the default value. You can also set the value to Standard or Adaptive. Standard represents the standardized request retry strategy which is consistent across all SDKs; Adaptive represents an experimental request retry strategy that builds on the Standard strategy and introduces congestion control through client-side rate limiting.
-
-
Click Save to save the custom storage location.
Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
Follow the instructions below:
*Note: Before adding the storage account to the Cloud Backup for Google Workspace interface, ensure AvePoint Agents have access to your storage. For details, refer to Allow AvePoint Agent Servers to Access Your Storage Account.
-
Storage type – Select Microsoft Azure Blob Storage from the drop-down list.
-
Access point – Enter the URL for the Blob Storage Service. The default URL is https://blob.core.windows.net.
-
Container name – Enter the name for the container you wish to access.
-
Account name – Enter the corresponding account name to access the specified container.
-
Account key – Enter the corresponding account key to access the specified container.
-
Advanced – If you want to configure extended parameters, select the Advanced option. Refer to the instructions below to configure Extended parameters, and note that if you have multiple parameters to enter, use the semicolon (;) to separate the parameters.
-
RetryInterval – Customize the retry interval when the network connection is interrupted. You are allowed to enter any positive integer from 0 to 2147483646 (the unit is in milliseconds). For example, RetryInterval=30000 means that it will try to reconnect every 30000 milliseconds.
If you do not configure this parameter, the value is 30000 milliseconds by default.
-
RetryCount – Customize the reconnection times after the network connection is interrupted. You are allowed to enter any positive integer from 0 to 2147483646. For example, RetryCount=10 represents when the network connection is interrupted, it can reconnect at most 10 times.
If you do not configure this parameter, the value is 6 by default.
-
-
Click Save to save the custom storage location.
IBM Storage Protect – S3
Follow the instructions below:
-
Storage type – Select IBM Storage Protect - S3 from the drop-down list.
-
Bucket name – Enter the bucket name you wish to access.
-
Access key ID – Enter the corresponding access key ID to access the specified bucket.
-
Secret access key – Enter the corresponding secret key ID to access the specified bucket.
-
Endpoint – Enter the URL used to connect to the place where you want to store the data.
*Note: The URL must begin with ‘’http://’’ or ‘’https://’’.
-
Advanced – If you want to configure extended parameters, select the Advanced option. Refer to the instructions below to configure Extended parameters, and note that if you have multiple parameters to enter, use the semicolon (;) to separate the parameters.
-
Use_PathStyle – The default value of this parameter is true to ensure the Cloud Backup for Google Workspace can work with your storage properly.
-
RetryCount – Customize the reconnection times after the network connection is interrupted. Enter any positive integer from 0 to 2147483646. For example, RetryCount=6 represents when the network connection is interrupted, and it can reconnect at most 6 times.
If you do not configure this parameter, the value is 6 by default.
-
RetryMode – Customize the retry mode for the requests not being completed successfully. If this parameter is not configured or configured incorrectly, the Legacy will be applied as the default value. You can also set the value to Standard or Adaptive. Standard represents the standardized request retry strategy which is consistent across all SDKs; Adaptive represents an experimental request retry strategy that builds on the Standard strategy and introduces congestion control through client-side rate limiting.
-
Allow_Insecure_SSL – By default, the storage client expects an SSL certificate issued by a public trusted certificate authority over HTTPS transport to ensure integrity. A self-signed certificate on the storage server side will fail the certificate validation. If you choose to use a self-signed certificate, you can set the Allow_Insecure_SSL to true in the Extended parameters to bypass the certificate validation.
-
Cert_thumbprint – If you use a self-signed certificate on the storage server side and you want to pass the certificate validation with a specific thumbprint, set the value to the thumbprint string.
By default, the Cert_thumbprint parameter is not configured.
-
-
Click Save to save the custom storage location.
IBM Cloud Object Storage
Follow the instructions below:
-
Storage type – Select IBM Cloud Object Storage from the drop-down list.
-
Bucket name – Enter the bucket name you wish to access.
-
Access key ID – Enter the corresponding access key ID to access the specified bucket.
-
Secret access key – Enter the corresponding secret key ID to access the specified bucket.
-
Endpoint – Enter the URL used to connect to the place where you want to store the data.
*Note: The URL must begin with “http://” or “https://”.
-
Advanced – If you want to configure extended parameters, select the Advanced option. Refer to the instructions below to configure Extended parameters, and note that if you have multiple parameters to enter, use the semicolon (;) to separate the parameters.
-
RetryCount – Customize the reconnection times after the network connection is interrupted. Enter any positive integer from 0 to 2147483646. For example, RetryCount=6 represents when the network connection is interrupted. It can reconnect at most 6 times.
If you do not configure this parameter, the value is 6 by default.
-
RetryMode – Customize the retry mode for the requests not being completed successfully. If this parameter is not configured or configured incorrectly, the Legacy will be applied as the default value. You can also set the value to Standard or Adaptive. Standard represents the standardized request retry strategy which is consistent across all SDKs; Adaptive represents an experimental request retry strategy that builds on the Standard strategy and introduces congestion control through client-side rate limiting.
-
-
Click Save to save the custom storage location.
